定时器理论
实际的业务场景会遇到许多使用定时任务的场景,定时器主要有三种表现形式:固定周期定时执行、延迟一定时间执行,指定某个时刻执行。再实现层面,定时器需要考虑存储和调度指定任务,内部通过轮询的方式检查任务是否到期并需要执行。
Java定时器
Java提供了三种常用的定时器实现方式:
- Timer
- DelayQueue
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
Timer
Timer使用的就是上述最原始的定时器实现方式:
- 存储:TaskQueue是数组实现的小根堆,deadline最近的任务位于堆顶端。
- 调度:TimerThread异步线程,定时轮询队列,如果堆顶任务的deadline已到,那么执行任务,如果是周期性任务,执行完计算下次deadline,并再次放入小根堆。
public class Timer {
private final TaskQueue queue = new TaskQueue();
private final TimerThread thread = new TimerThread(queue);
public Timer(String name) {
thread.setName(name);
thread.start();
}
}
Timer存在几个缺陷:
- 单线程模式,某个TimeTask阻塞,会影响其他的任务调度。
- Timer的任务调度基于系统时间的,系统时间不正确,可能出现问题。
- TimeTask执行出现异常,Timer不会捕获,线程终止后,其他任务都不能执行。
使用案例:
Timer timer = new Timer();
//设置一个10s后调度一个周期为1s的定时任务
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
// do something
}
}, 10000, 1000);
DelayQueue
DelayQueue是一种可以延迟获取对象的阻塞队列,内部使用PriorityQueue存储任务,每个元素必须实现Delayed接口,并重写指定方法。DelayQueue提供了put和take两个阻塞方法。对象put进去后,通过compareTo进行优先级排序,getDelay计算出剩余时间,只有小于等于0时,对象才能从其中被取出。
实际上只实现了存储定时任务的功能,还需要配合异步线程才能实现定时器。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
该线程池继承于ThreadPoolExecutor,提供了周期执行和延迟执行的功能,在ThreadPoolExecutor的基础上,重新设计了任务ScheduledFutureTask和阻塞队列DelayedWorkQueue。
- ScheduledFutureTask:继承于FutureTask,重写run方法,使其具有周期执行任务的能力。
- DelayedWorkQueue:优先级队列,deadline最近的任务在头部,周期任务执行完重设事件,再次放入队列。
以上三种定时器在面临海量任务的插入删除都存在性能瓶颈,时间轮算法可以解决相应的性能问题。
时间轮结构
如下图所示,时间轮可以理解成环型队列,每个元素代表一个时间段(slot),并且能存放多个任务,同一个时间段中的任务通过链表保存,时间轮随着时间变化,时针指向一个个区间,并执行区间内所有任务。
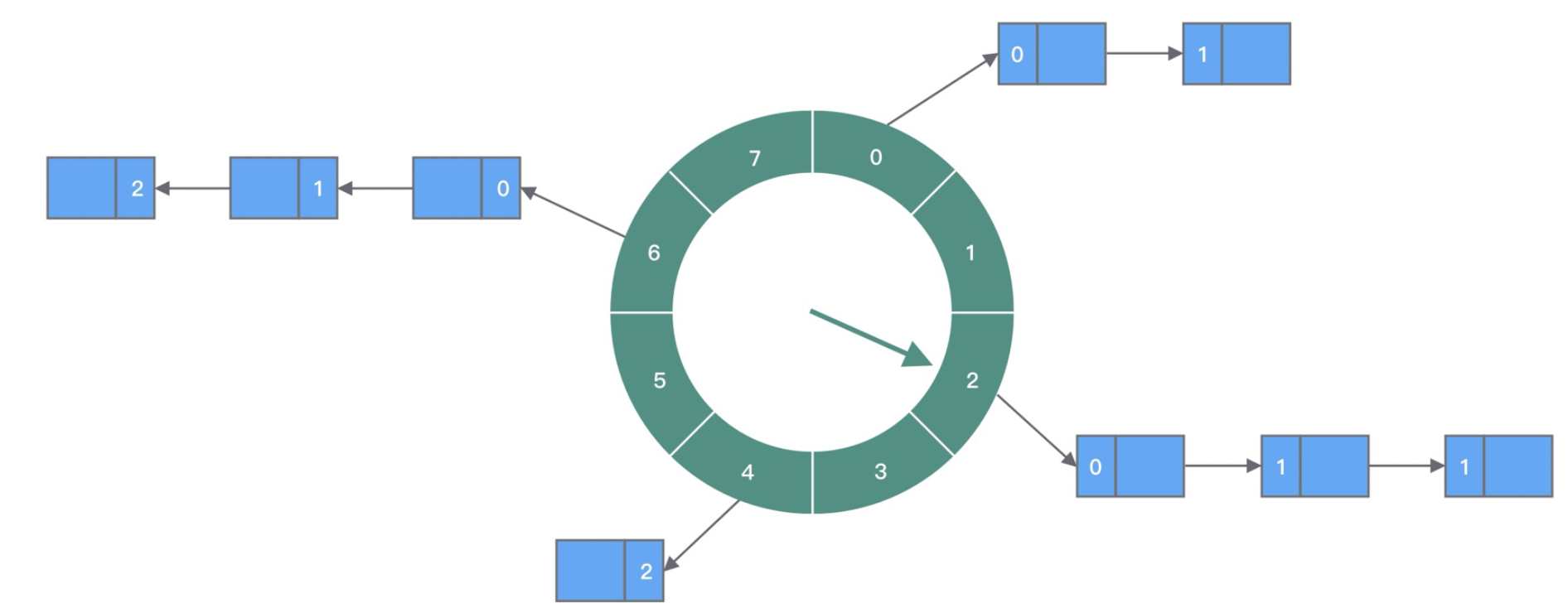
HashedWheelTimer
接口关系
HashedWheelTimer是Netty中的时间轮算法的实现类。其实现了Timer接口,该接口提供了两个方法:
- newTimeout:创建定时任务
- stop:停止所有未执行的定时任务
HashedWheelTimer类图如下所示:
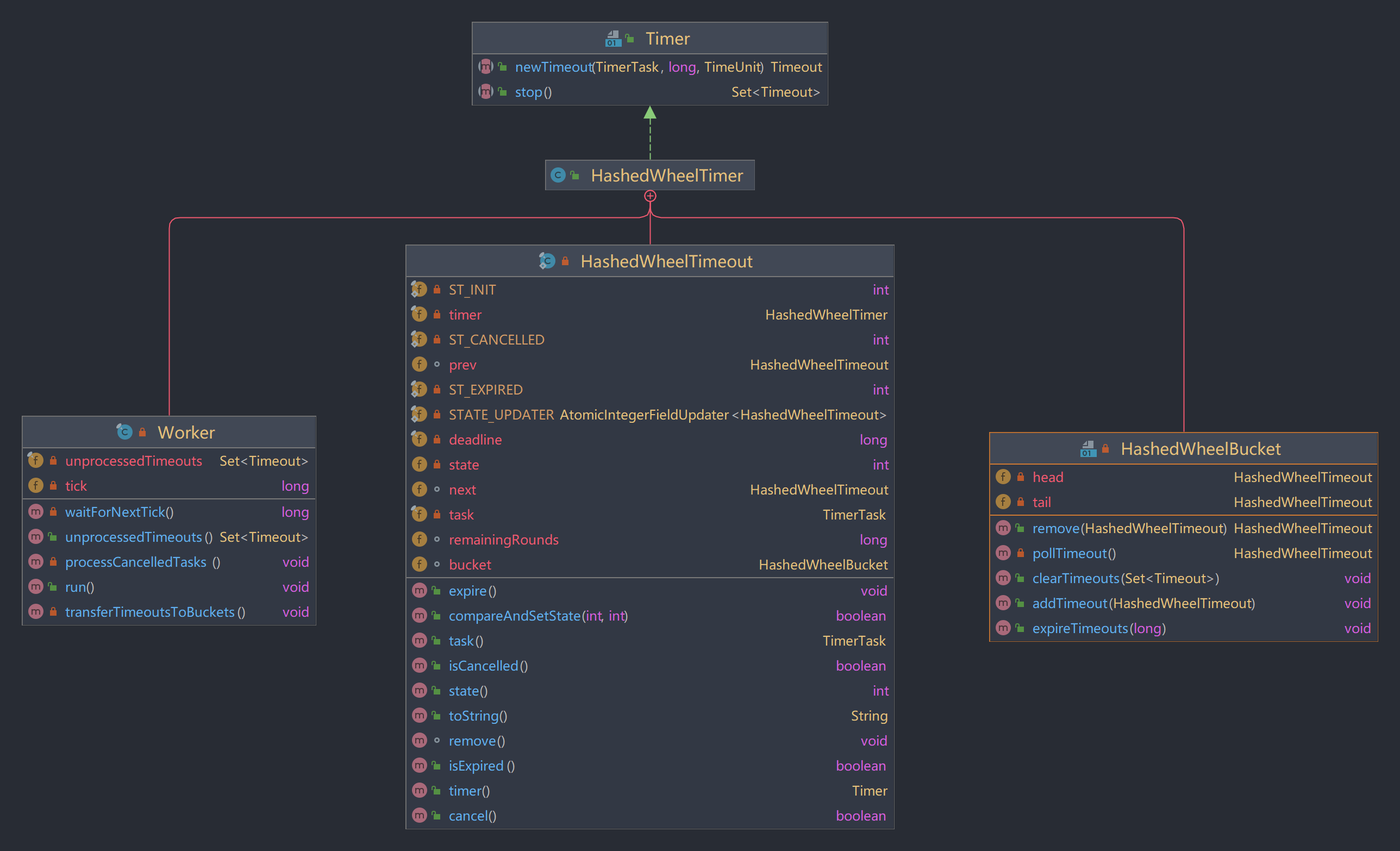
Timer中使用的TimerTask和Timeout是两个接口,分别定义如下:
public interface TimerTask {
void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception;
}
public interface Timeout {
Timer timer();
TimerTask task();
boolean isExpired();
boolean isCancelled();
boolean cancel();
}
构造方法
public HashedWheelTimer(
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
long tickDuration, TimeUnit unit, int ticksPerWheel, boolean leakDetection,
long maxPendingTimeouts)
核心属性如下:
- threadFactory:线程池,只创建了一个线程。
- tickDuration:时针移动的单位,相当于时间段长度。
- unit:tickDuration的时间单位。
- ticksPerWheel:时间轮上的slot数量,默认为512个。
- leakDetection:是否开启内存泄漏检测
- maxPendingTimeouts:最大允许等待的任务数量。
createWheel-时间轮初始化
createWheel方法是HashedWheelTimer构造方法中用来创建HashedWheelBucket数组,该数组就是时间轮,内部是一个双向链表,存储的元素为HashedWheelTimeout,这代表的是定时任务。
private static HashedWheelBucket[] createWheel(int ticksPerWheel) {
// 省略其他代码
ticksPerWheel = normalizeTicksPerWheel(ticksPerWheel);
HashedWheelBucket[] wheel = new HashedWheelBucket[ticksPerWheel];
for (int i = 0; i < wheel.length; i ++) {
wheel[i] = new HashedWheelBucket();
}
return wheel;
}
//找到不小于ticksPerWheel的最小2次幂
private static int normalizeTicksPerWheel(int ticksPerWheel) {
int normalizedTicksPerWheel = 1;
while (normalizedTicksPerWheel < ticksPerWheel) {
normalizedTicksPerWheel <<= 1;
}
return normalizedTicksPerWheel;
}
private static final class HashedWheelBucket {
private HashedWheelTimeout head;
private HashedWheelTimeout tail;
}
newTimeout-创建定时任务
该方法用于往时间轮添加任务,主要有三个流程:
- 启动工作线程
- 创建定时任务
- 把HashedWheelTimeout任务添加到Mpsc Queue
- Mpsc Queue是线程安全的队列,借助该队列保证添加任务的线程安全性。
public Timeout newTimeout(TimerTask task, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(task, "task");
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(unit, "unit");
long pendingTimeoutsCount = pendingTimeouts.incrementAndGet();
if (maxPendingTimeouts > 0 && pendingTimeoutsCount > maxPendingTimeouts) {
pendingTimeouts.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Number of pending timeouts ("
+ pendingTimeoutsCount + ") is greater than or equal to maximum allowed pending "
+ "timeouts (" + maxPendingTimeouts + ")");
}
//启动工作线程
start();
// Add the timeout to the timeout queue which will be processed on the next tick.
// During processing all the queued HashedWheelTimeouts will be added to the correct HashedWheelBucket.
long deadline = System.nanoTime() + unit.toNanos(delay) - startTime;
// Guard against overflow.
if (delay > 0 && deadline < 0) {
deadline = Long.MAX_VALUE;
}
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = new HashedWheelTimeout(this, task, deadline);
timeouts.add(timeout);
return timeout;
}
private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<HashedWheelTimer> WORKER_STATE_UPDATER =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(HashedWheelTimer.class, "workerState");
public void start() {
//获取工作线程的状态
switch (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(this)) {
case WORKER_STATE_INIT:
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, WORKER_STATE_INIT, WORKER_STATE_STARTED)) {
workerThread.start();
}
break;
case WORKER_STATE_STARTED:
break;
case WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN:
throw new IllegalStateException("cannot be started once stopped");
default:
throw new Error("Invalid WorkerState");
}
// Wait until the startTime is initialized by the worker.
while (startTime == 0) {
try {
startTimeInitialized.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ignore) {
// Ignore - it will be ready very soon.
}
}
}
Worker-执行引擎
worker是负责执行任务的,实现了Runnable接口,工作线程通过workerThread = threadFactory.newThread(worker);来创建。执行流程如下:
- waitForNextTick计算出下次tick时间,sleep到下次tick
- 计算当前tick在时间轮中的对应下标
- 移除被取消的任务
- 执行当前时间轮的到期任务
private final class Worker implements Runnable {
private final Set<Timeout> unprocessedTimeouts = new HashSet<Timeout>();
private long tick;
@Override
public void run() {
// Initialize the startTime.
startTime = System.nanoTime();
if (startTime == 0) {
// We use 0 as an indicator for the uninitialized value here, so make sure it's not 0 when initialized.
startTime = 1;
}
// Notify the other threads waiting for the initialization at start().
startTimeInitialized.countDown();
do {
//计算下次tick时间
final long deadline = waitForNextTick();
if (deadline > 0) {
//获取当前tick在时间轮中的下标
int idx = (int) (tick & mask);
//移除被取消的任务
processCancelledTasks();
HashedWheelBucket bucket =
wheel[idx];
//从Mpsc Queue取出任务,加入slot
transferTimeoutsToBuckets();
//执行所有到期的任务
bucket.expireTimeouts(deadline);
tick++;
}
} while (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(HashedWheelTimer.this) == WORKER_STATE_STARTED);
// Fill the unprocessedTimeouts so we can return them from stop() method.
for (HashedWheelBucket bucket: wheel) {
bucket.clearTimeouts(unprocessedTimeouts);
}
for (;;) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = timeouts.poll();
if (timeout == null) {
break;
}
if (!timeout.isCancelled()) {
unprocessedTimeouts.add(timeout);
}
}
processCancelledTasks();
}