简介
字典是一种用来存储键值对的数据结构。Redis本身就是KV型数据库,整个数据库就是用字典进行存储的,对Redis的增删改查操作,实际上就是对字典中的数据进行增删改查操作。
数据结构
HashTable
- table:指针数组,用于存储键值对,指向的是
dictEntry结构体,每个dictEntry存有键值对 - size:table数组的大小
- sizemask:掩码,用来计算键的索引值。值恒为size -1
- used:table数组已存键值对个数
Hash表的数组容量初始值为4,扩容倍数为当前一倍,所以sizemask大小为3,7,11,31,二进制表示为111111...,在计算索引值时,首先计算hash值,通过hash = dict-> type->hashFunction(k0)得到对应hash。再通过idx = hash & d->dt[table].sizemask计算entry存储的索引位置,位运算速度快于取余运算,Redis使用链地址法来解决hash冲突问题。
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
rehash
hashtable一般需要将负载因子维护在一个合理的范围,使得其达到最大的操作效率,当键值对数量太多或太少时,都需要对hashtable进行相应的扩展或缩容。rehash动作是分批次、渐进式完成的,这是为了避免rehash对server性能造成影响。
Redis进行rehash的执行步骤如下:
- 为
ht[1]分配空间,空间大小取决于ht[0]包含的键值对数量。 - 将所有保存在
ht[0]的键值对rehash到ht[1]上,即重新计算对应hash和index,并存储在ht[1] - 释放
ht[0]空间,将ht[1]设置为ht[0],并在ht[1]新建一个空白hashtable,为下一次rehash服务。
在渐进式rehash过程中,查询等操作同时使用两个hashtable。
dictEntry
键值对节点,存放键值对数据。
typedef struct dictEntry {
//键
void *key;
union {
//存储值
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
//存储过期时间
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;//值,联合体
//next指针,Hash冲突时的单链表法
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
dictType
存放的是对字典操作的函数指针
typedef struct dictType {
//Hash函数,默认使用MurmurHash2算法来计算hash值
uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
//键对应的复制函数
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
//值对应的复制函数
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
//键的比对函数
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
//键的销毁函数
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
//值得销毁函数
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
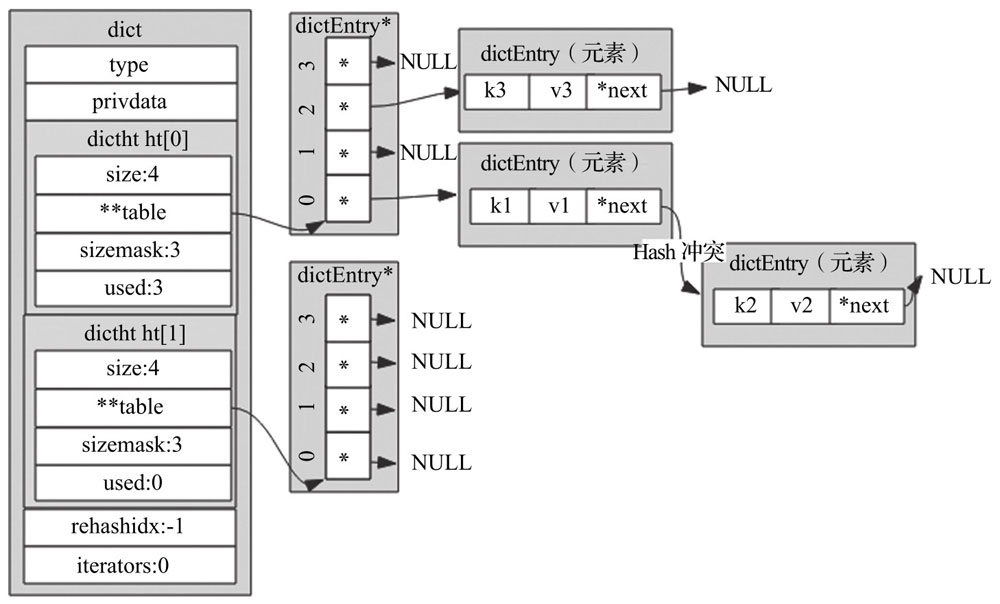
dict
- type:字典操作函数指针,指向一个dictType结构的指针
- privdata:私有数据,配合tyoe指针指向的函数一起使用
- ht:大小为2的数组,默认使用ht[0],当字典扩容缩容时进行rehash时,才会用到ht[1]
- rehashidx:标记该字典是否在进行rehash,没进行为-1,用来记录rehash到了哪个元素,值为下标值
- iterators:用来记录当前运行的安全迭代器数,当有安全迭代器,会暂停rehash
基本结构图如图所示:
typedef struct dict {
//存放字典的操作函数
dictType *type;
//依赖的数据
void *privdata;
//Hash表
dictht ht[2];
//rehash标识,默认为-1,代表没有进行rehash操作
long rehashidx;
//当前运行的迭代器数
unsigned long iterators;
} dict;
接口
dictCreate
redis-server启动时,会初始化一个空字典用于存储整个数据库的键值对,初始化的主要逻辑如下:
- 申请空间
- 调用
_dictInit完成初始化
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d));
_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr);
return d;
}
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
_dictReset(&d->ht[0]);
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->type = type;
d->privdata = privDataPtr;
d->rehashidx = -1;
d->iterators = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
dictAdd
添加键值对,主要逻辑如下:
- 调用
dictAddRaw,添加键 - 给返回的新节点设置值(更新val字段)
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
//添加键,字典中键已存在则返回NULL,否则添加新节点,并返回
dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key,NULL);
//键存在则添加错误
if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;
//设置值
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
return DICT_OK;
}
//d为入参字典,key为键,existing为Hash表节点地址
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key, dictEntry **existing)
{
long index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
//字典是否在进行rehash操作
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
//查找键,找到直接返回-1,并把老节点存放在existing里,否则返回新节点索引值
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key, dictHashKey(d,key), existing)) == -1)
return NULL;,
//检测容量
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
//申请新节点内存空间,插入哈希表
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
entry->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = entry;
ht->used++;
//存储键信息
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}
dictExpand
扩容操作主要逻辑:
- 计算扩容大小(是size的下一个2的幂)
- 将新申请的地址存放于ht[1],并把
rehashidx标为1,表示需要进行rehash
扩容完成后ht[1]中为全新的Hash表,扩容之后,添加操作的键值对全部存放于全新的Hash表中,修改删除查找等操作需要在ht[0]和ht[1]中进行检查。此外还需要将ht[0]中的键值对rehash到ht[1]中。
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size)
{
//如果已存在空间大于传入size,则无效
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)
return DICT_ERR;
dictht n; /* the new hash table */
//扩容值为2的幂
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
//相同则不扩容
if (realsize == d->ht[0].size) return DICT_ERR;
//将新的hash表内部变量初始化,并申请对应的内存空间
n.size = realsize;
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = 0;
//如果当前是空表,就直接存放在ht[0]
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
扩容后的新内存放入ht[1]
d->ht[1] = n;
//表示需要进行rehash
d->rehashidx = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
dictResize
缩容操作主要通过dictExpand(d, minimal)实现。
#define DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE 4
int dictResize(dict *d)
{
int minimal;
//判断是否在rehash
if (!dict_can_resize || dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_ERR;
//minimal为ht[0]的已使用量
minimal = d->ht[0].used;
//如果键值对数量 < 4,将缩容至4
if (minimal < DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE)
minimal = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
//调用dictExpand进行缩容
return dictExpand(d, minimal);
}
Rehash
Rehash在缩容和扩容时都会触发。执行插入、删除、查找、修改操作前,会判断当前字典是否在rehash,如果在,调用dictRehashStep进行rehash(只对一个节点rehash)。如果服务处于空闲时,也会进行rehash操作(incrementally批量,一次100个节点)
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
//如果已经rehash结束,直接返回
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
//找到hash表中不为空的位置
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
//de为rehash标识,存放正在进行rehash节点的索引值
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;
//h
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
//插入
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
//更新数据
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
de = nextde;
}
//置空
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
//检查是否已经rehash过了
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
/* More to rehash... */
return 1;
}
dictFind
查找键的逻辑较为简单,遍历ht[0]和ht[1]。
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key)
{
dictEntry *he;
uint64_t h, idx, table;
//字典为空,直接返回
if (d->ht[0].used + d->ht[1].used == 0) return NULL; /* dict is empty */
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
//获取键的hash值
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
//遍历查找hash表,ht[0]和ht[1]
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
//遍历单链表
while(he) {
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}
dictDelete
删除的主要逻辑如下:
- 查找该键是否存在于该字典中
- 存在则将节点从单链表中删除
- 释放节点内存空间,used减一
int dictDelete(dict *ht, const void *key) {
return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,0) ? DICT_OK : DICT_ERR;
}
static dictEntry *dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree) {
uint64_t h, idx;
dictEntry *he, *prevHe;
int table;
//如果字典为空直接返回
if (d->ht[0].used == 0 && d->ht[1].used == 0) return NULL;
//。如果正在rehash,则调用_dictRehashStep进行rehash一次
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
//获取需要删除节点的键Hash值
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
//从ht[0]和ht[1]中查找
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
prevHe = NULL;
//遍历单链表查找
while(he) {
if (key==he->key || dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) {
//删除节点
if (prevHe)
prevHe->next = he->next;
else
d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next;
if (!nofree) {
//释放节点内存空间
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
zfree(he);
}
//used自减一
d->ht[table].used--;
return he;
}
prevHe = he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return NULL; /* not found */
}
总结
本文主要对Redis中的字典基本结构做了简要分析,对字典的创建,键值对添加/删除/查找等操作与字典的缩容扩容机制做了简要分析,键值对修改操作主要通过db.c中的dbOverwrite函数调用dictSetVal实现。
字典是通过两个hashtable来实现的,一个用于日常存储,一个用于渐进式rehash,字典被应用于提供的hash结构和服务端的数据库存储。