Consumer
Consumer作为Kafka Clients中的消费者,继承关系如下图所示:
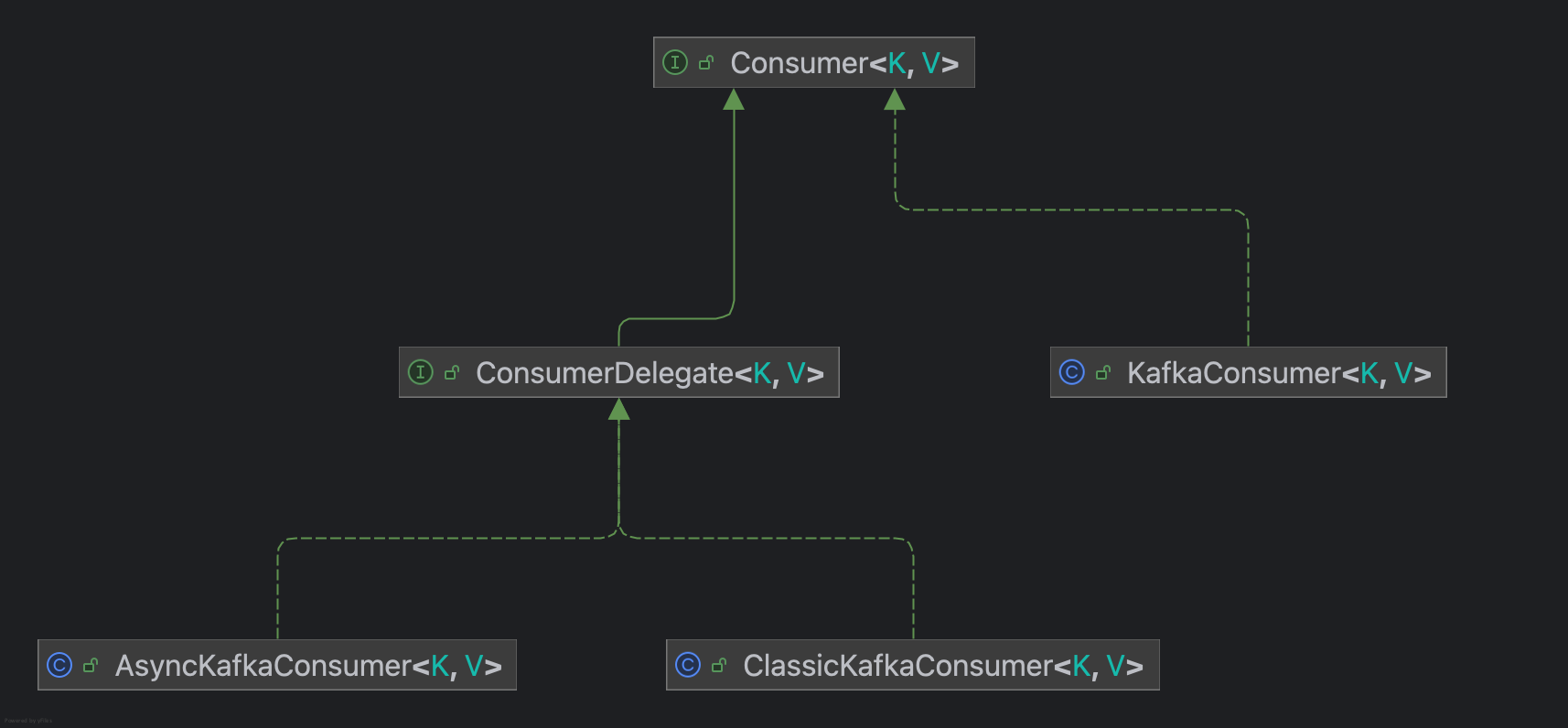
KafkaConsumer作为Facade类,提供API供clients使用,而ConsumerDelegate作为实现类接口,提供了两种实现方式,通过配置group.protocol进行控制,其中ClassicKafkaConsumer所有的线程都会处理网络IO请求,AsyncKafkaConsumer则是基于Reactor模式,使用单独线程处理网络IO,以事件驱动模式处理任务,具体细节见 Consumer threading refactor design。
本次分析也以AsyncKafkaConsumer为例。
KafkaConsumer内置的成员变量如下:
//用于创建delegate的工厂类
private static final ConsumerDelegateCreator CREATOR = new ConsumerDelegateCreator();
//consumer具体的实现类
private final ConsumerDelegate<K, V> delegate;
初始化方法:
KafkaConsumer(ConsumerConfig config, Deserializer<K> keyDeserializer, Deserializer<V> valueDeserializer) {
delegate = CREATOR.create(config, keyDeserializer, valueDeserializer);
}
public <K, V> ConsumerDelegate<K, V> create(ConsumerConfig config,
Deserializer<K> keyDeserializer,
Deserializer<V> valueDeserializer) {
try {
//根据配置选取对应的实现类
GroupProtocol groupProtocol = GroupProtocol.valueOf(config.getString(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_PROTOCOL_CONFIG).toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT));
if (groupProtocol == GroupProtocol.CONSUMER)
return new AsyncKafkaConsumer<>(config, keyDeserializer, valueDeserializer);
else
return new ClassicKafkaConsumer<>(config, keyDeserializer, valueDeserializer);
} catch (KafkaException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new KafkaException("Failed to construct Kafka consumer", t);
}
}
事件处理逻辑
AsyncKafkaConsumer的核心使用事件驱动模式来处理各类事件,具体事件类型见org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.internals.events.ApplicationEvent
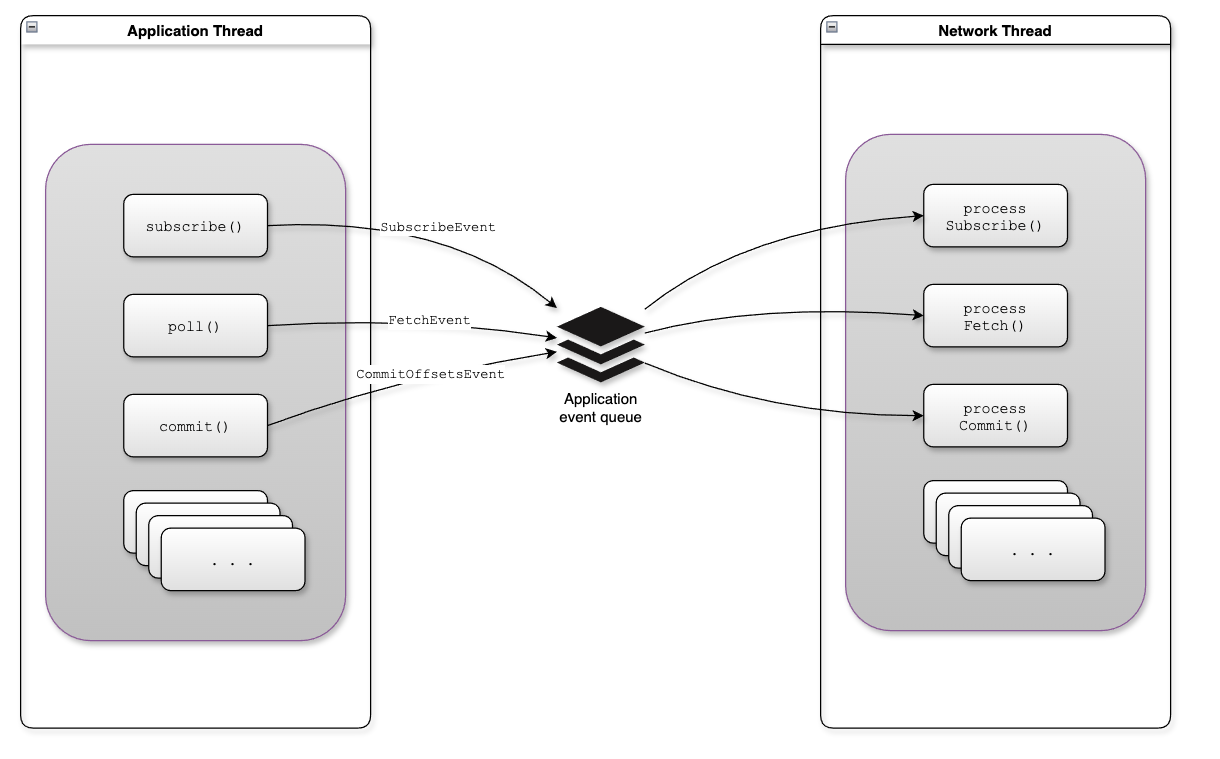
ApplicationEventHandler
ApplicationEventHandler用于接收来自consumer端的各类事件,属性和构造方法如下:
// 用于接收application event的BlockingQueue
private final BlockingQueue<ApplicationEvent> applicationEventQueue;
//网络IO线程
private final ConsumerNetworkThread networkThread;
public ApplicationEventHandler(final LogContext logContext,
final Time time,
final BlockingQueue<ApplicationEvent> applicationEventQueue,
final CompletableEventReaper applicationEventReaper,
final Supplier<ApplicationEventProcessor> applicationEventProcessorSupplier,
final Supplier<NetworkClientDelegate> networkClientDelegateSupplier,
final Supplier<RequestManagers> requestManagersSupplier) {
this.log = logContext.logger(ApplicationEventHandler.class);
this.applicationEventQueue = applicationEventQueue;
this.networkThread = new ConsumerNetworkThread(logContext,
time,
applicationEventQueue,
applicationEventReaper,
applicationEventProcessorSupplier,
networkClientDelegateSupplier,
requestManagersSupplier);
this.networkThread.start();
}
核心方法add()用于向event queue追加事件,并唤醒网络IO线程。
public void add(final ApplicationEvent event) {
Objects.requireNonNull(event, "ApplicationEvent provided to add must be non-null");
applicationEventQueue.add(event);
wakeupNetworkThread();
}
ApplicationEventProcessor
ApplicationEventProcessor是实际处理各类application event的执行器:
@Override
public void process(ApplicationEvent event) {
switch (event.type()) {
case COMMIT_ASYNC:
process((AsyncCommitEvent) event);
return;
……
}
}
以AsyncCommitEvent为例,通过requestManagers容器获取到对应职责的RequestManager,并将request追加到pendingRequests,由ConsumerNetworkThread调用poll()获取unsent请求,并通过实际与broker交互的KafkaClient发送request并处理。
private void process(final AsyncCommitEvent event) {
if (!requestManagers.commitRequestManager.isPresent()) {
return;
}
CommitRequestManager manager = requestManagers.commitRequestManager.get();
CompletableFuture<Void> future = manager.commitAsync(event.offsets());
future.whenComplete(complete(event.future()));
}
ConsumerNetworkThread
ConsumerNetworkThread是用于后台处理event的线程,并负责处理broker的网络IO。
线程的run()方法通过while循环循环调用runOnce()。
public void run() {
try {
log.debug("Consumer network thread started");
// Wait until we're securely in the background network thread to initialize these objects...
initializeResources();
while (running) {
try {
runOnce();
} catch (final Throwable e) {
// Swallow the exception and continue
log.error("Unexpected error caught in consumer network thread", e);
}
}
} finally {
cleanup();
}
}
runOnce()方法主要处理以下几个任务:
- 提取event并使用ApplicationEventProcessor处理application event
- 遍历RequestManager并调用poll()方法
- 调用NetworkClientDelegate. addAll(List)将request添加到unsentRequests队列中
- 调用KafkaClient. poll(long, long)向broker发送请求
void runOnce() {
//1.1 通过ApplicationEventProcessor处理各类event
processApplicationEvents();
final long currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
final long pollWaitTimeMs = requestManagers.entries().stream()
.filter(Optional::isPresent)
.map(Optional::get)
//1.2 循环调用RequestManager.poll(long)获取unsentRequests
.map(rm -> rm.poll(currentTimeMs))
//1.3 调用addAll,将unsentRequests添加到NetworkClientDelegate中
.map(networkClientDelegate::addAll)
.reduce(MAX_POLL_TIMEOUT_MS, Math::min);
//1.4 调用poll,发送请求,接收响应
networkClientDelegate.poll(pollWaitTimeMs, currentTimeMs);
cachedMaximumTimeToWait = requestManagers.entries().stream()
.filter(Optional::isPresent)
.map(Optional::get)
.map(rm -> rm.maximumTimeToWait(currentTimeMs))
.reduce(Long.MAX_VALUE, Math::min);
//1.5 清理过期event
reapExpiredApplicationEvents(currentTimeMs);
}
processApplicationEvents()用于通过applicationEventProcessor来处理event。
/**
* Process the events—if any—that were produced by the application thread. */private void processApplicationEvents() {
//1.1 获取queue中所有 event LinkedList<ApplicationEvent> events = new LinkedList<>();
applicationEventQueue.drainTo(events);
//1.2 循环遍历,通过applicationEventProcessor处理event
for (ApplicationEvent event : events) {
try {
if (event instanceof CompletableEvent)
applicationEventReaper.add((CompletableEvent<?>) event);
applicationEventProcessor.process(event);
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.warn("Error processing event {}", t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
}
BackgroundEventProcessor
BackgroundEventProcessor作为AsyncKafkaConsumer成员变量,用于处理network thread产生的background events,从其process()方法中可以看出,该processor主要处理以下事件:
- network thread产生的error event
- 在application thread执行rebalance回调逻辑
public void process(final BackgroundEvent event) {
switch (event.type()) {
case ERROR:
process((ErrorEvent) event);
break;
case CONSUMER_REBALANCE_LISTENER_CALLBACK_NEEDED:
process((ConsumerRebalanceListenerCallbackNeededEvent) event);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Background event type " + event.type() + " was not expected");
}
}
订阅主题
subscribe方法来订阅主题,若多次调用,以最后一次作为消费的主题。
public void subscribe(Collection<String> topics, ConsumerRebalanceListener listener) {
if (listener == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("RebalanceListener cannot be null");
subscribeInternal(topics, Optional.of(listener));
}
subscribeInternal()方法用于处理实际的subscribe逻辑。
private void subscribeInternal(Collection<String> topics, Optional<ConsumerRebalanceListener> listener) {
//1.1 获取lock,并且判断是否已经close
acquireAndEnsureOpen();
try {
//1.2 判断group id是否有效
maybeThrowInvalidGroupIdException();
//1.3 校验参数
if (topics == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Topic collection to subscribe to cannot be null");
//1.4 若为空,则unsubscribe
if (topics.isEmpty()) {
// treat subscribing to empty topic list as the same as unsubscribing
unsubscribe();
} else {
for (String topic : topics) {
if (isBlank(topic))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Topic collection to subscribe to cannot contain null or empty topic");
}
// 1.5 更新buffer中不再指定的partition
final Set<TopicPartition> currentTopicPartitions = new HashSet<>();
for (TopicPartition tp : subscriptions.assignedPartitions()) {
if (topics.contains(tp.topic()))
currentTopicPartitions.add(tp);
}
fetchBuffer.retainAll(currentTopicPartitions);
log.info("Subscribed to topic(s): {}", String.join(", ", topics));
// 1.6 调用SubscriptionState.subscribe 更新订阅topic
if (subscriptions.subscribe(new HashSet<>(topics), listener))
//若请求成功,更新metadata
this.metadataVersionSnapshot = metadata.requestUpdateForNewTopics();
// 1.7 向handler添加event
applicationEventHandler.add(new SubscriptionChangeEvent());
}
} finally {
//1.8 释放lock
release();
}
}
加锁方式采用乐观锁,校验内置threadId是否一致:
private void acquire() {
final Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
final long threadId = thread.getId();
if (threadId != currentThread.get() && !currentThread.compareAndSet(NO_CURRENT_THREAD, threadId))
throw new ConcurrentModificationException("KafkaConsumer is not safe for multi-threaded access. " +
"currentThread(name: " + thread.getName() + ", id: " + threadId + ")" +
" otherThread(id: " + currentThread.get() + ")"
);
refCount.incrementAndGet();
}
取消订阅
unsubscribe()方法用于取消topic订阅。
public void unsubscribe() {
//1.1 获取锁,并确保当前消费者没有关闭
acquireAndEnsureOpen();
try {
//1.2 删除buffer中所有订阅的topic分区
fetchBuffer.retainAll(Collections.emptySet());
Timer timer = time.timer(Long.MAX_VALUE);
//1.3 向handler发送unsubscribeEvent
UnsubscribeEvent unsubscribeEvent = new UnsubscribeEvent(calculateDeadlineMs(timer));
applicationEventHandler.add(unsubscribeEvent);
log.info("Unsubscribing all topics or patterns and assigned partitions {}",
subscriptions.assignedPartitions());
//1.4 循环处理background event
try {
processBackgroundEvents(unsubscribeEvent.future(), timer);
log.info("Unsubscribed all topics or patterns and assigned partitions");
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
log.error("Failed while waiting for the unsubscribe event to complete");
}
//1.5 重置group的metadata
resetGroupMetadata();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Unsubscribe failed", e);
throw e;
} finally {
//1.6 释放lock
release();
}
}
拉取消息
poll()方法传递timeout,在指定timeout内,从broker消费数据。
public ConsumerRecords<K, V> poll(final Duration timeout) {
Timer timer = time.timer(timeout);
//1.1 获取lock并确保consumer未关闭
acquireAndEnsureOpen();
try {
//1.2 更新consumer监控指标
kafkaConsumerMetrics.recordPollStart(timer.currentTimeMs());
//1.3 确保已订阅topic
if (subscriptions.hasNoSubscriptionOrUserAssignment()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Consumer is not subscribed to any topics or assigned any partitions");
}
//1.4 定时处理poll逻辑
do {
// 1.5 向handler发送PollEvent
applicationEventHandler.add(new PollEvent(timer.currentTimeMs()));
// We must not allow wake-ups between polling for fetches and returning the records.
// If the polled fetches are not empty the consumed position has already been updated in the polling // of the fetches. A wakeup between returned fetches and returning records would lead to never // returning the records in the fetches. Thus, we trigger a possible wake-up before we poll fetches. wakeupTrigger.maybeTriggerWakeup();
//1.6 更新metadata,并唤醒network thread处理poll任务,获取数据
updateAssignmentMetadataIfNeeded(timer);
final Fetch<K, V> fetch = pollForFetches(timer);
if (!fetch.isEmpty()) {
if (fetch.records().isEmpty()) {
log.trace("Returning empty records from `poll()` "
+ "since the consumer's position has advanced for at least one topic partition");
}
//1.6 通过interceptors处理前置消费逻辑,并返回ConsumerRecords
return interceptors.onConsume(new ConsumerRecords<>(fetch.records()));
}
// We will wait for retryBackoffMs
} while (timer.notExpired());
return ConsumerRecords.empty();
} finally {
//1.7 更新consumer监控指标,释放lock
kafkaConsumerMetrics.recordPollEnd(timer.currentTimeMs());
release();
}
}
collectFetch()方法从buffer中获取消息,其中FetchBuffer用于存储来自broker响应的消息结果CompletedFetch,每个CompletedFetch代表来自一个partition的响应结果。
public Fetch<K, V> collectFetch(final FetchBuffer fetchBuffer) {
final Fetch<K, V> fetch = Fetch.empty();
final Queue<CompletedFetch> pausedCompletedFetches = new ArrayDeque<>();
int recordsRemaining = fetchConfig.maxPollRecords;
try {
while (recordsRemaining > 0) {
//1.1 从fetchBuffer获取CompletedFetch
final CompletedFetch nextInLineFetch = fetchBuffer.nextInLineFetch();
//1.2 若nextInLineFetch()返回null或已被消费,从queue中获取
if (nextInLineFetch == null || nextInLineFetch.isConsumed()) {
final CompletedFetch completedFetch = fetchBuffer.peek();
//1.3 此时为空,说明broker暂无消息响应
if (completedFetch == null)
break;
//1.4 初始化CompletedFetch
if (!completedFetch.isInitialized()) {
try {
fetchBuffer.setNextInLineFetch(initialize(completedFetch));
} catch (Exception e) {
// Remove a completedFetch upon a parse with exception if (1) it contains no completedFetch, and
// (2) there are no fetched completedFetch with actual content preceding this exception. // The first condition ensures that the completedFetches is not stuck with the same completedFetch // in cases such as the TopicAuthorizationException, and the second condition ensures that no // potential data loss due to an exception in a following record.
if (fetch.isEmpty() && FetchResponse.recordsOrFail(completedFetch.partitionData).sizeInBytes() == 0)
fetchBuffer.poll();
throw e;
}
} else {
fetchBuffer.setNextInLineFetch(completedFetch);
}
fetchBuffer.poll();
//1.5 检查当前topic partition是否被暂停消费
} else if (subscriptions.isPaused(nextInLineFetch.partition)) {
// when the partition is paused we add the records back to the completedFetches queue instead of draining
// them so that they can be returned on a subsequent poll if the partition is resumed at that time
log.debug("Skipping fetching records for assigned partition {} because it is paused", nextInLineFetch.partition);
pausedCompletedFetches.add(nextInLineFetch);
fetchBuffer.setNextInLineFetch(null);
} else {
//1.6 从CompletedFetch中获取Fetch
final Fetch<K, V> nextFetch = fetchRecords(nextInLineFetch, recordsRemaining);
recordsRemaining -= nextFetch.numRecords();
fetch.add(nextFetch);
}
}
} catch (KafkaException e) {
if (fetch.isEmpty())
throw e;
} finally {
// add any polled completed fetches for paused partitions back to the completed fetches queue to be
// re-evaluated in the next poll
fetchBuffer.addAll(pausedCompletedFetches);
}
return fetch;
}
提交位移
commit提供了同步、异步两种方式:
/**
* Commit offsets returned on the last {@link #poll(Duration) poll()} for all the subscribed list of topics and
* partitions. */@Override
public void commitSync() {
commitSync(Duration.ofMillis(defaultApiTimeoutMs));
}
/**
* This method sends a commit event to the EventHandler and return. */@Override
public void commitAsync() {
commitAsync(null);
}
两者区别在于commitSync()会调用future.get()进行等待,而commitAsync()则调用whenComplete()执行异步回调。
@Override
public void commitSync(Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets, Duration timeout) {
//1.1 获取lock
acquireAndEnsureOpen();
long commitStart = time.nanoseconds();
try {
//1.2 向applicationEventHandler提交SyncCommitEvent
SyncCommitEvent syncCommitEvent = new SyncCommitEvent(offsets, calculateDeadlineMs(time, timeout));
CompletableFuture<Void> commitFuture = commit(syncCommitEvent);
//1.3 检查是否有lastPendingAsyncCommit任务需要执行
Timer requestTimer = time.timer(timeout.toMillis());
awaitPendingAsyncCommitsAndExecuteCommitCallbacks(requestTimer, true);
//1.4 将commitFuture配置到wakeupTrigger,调用future.get()等待完成
wakeupTrigger.setActiveTask(commitFuture);
ConsumerUtils.getResult(commitFuture, requestTimer);
//1.5 检查拦截器,执行前置commit方法
interceptors.onCommit(offsets);
} finally {
wakeupTrigger.clearTask();
kafkaConsumerMetrics.recordCommitSync(time.nanoseconds() - commitStart);
release();
}
}
@Override
public void commitAsync(Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets, OffsetCommitCallback callback) {
//1.1 获取lock
acquireAndEnsureOpen();
try {
//1.2 创建异步提交事件,并提交到EventHandler
AsyncCommitEvent asyncCommitEvent = new AsyncCommitEvent(offsets);
lastPendingAsyncCommit = commit(asyncCommitEvent).whenComplete((r, t) -> {
if (t == null) {
offsetCommitCallbackInvoker.enqueueInterceptorInvocation(offsets);
}
if (t instanceof FencedInstanceIdException) {
asyncCommitFenced.set(true);
}
if (callback == null) {
if (t != null) {
log.error("Offset commit with offsets {} failed", offsets, t);
}
return;
}
offsetCommitCallbackInvoker.enqueueUserCallbackInvocation(callback, offsets, (Exception) t);
});
} finally {
release();
}
}
核心用于构建CompletableFuture的commit方法如下:
private CompletableFuture<Void> commit(final CommitEvent commitEvent) {
//1.1 检查是否抛出异常
maybeThrowInvalidGroupIdException();
maybeThrowFencedInstanceException();
//1.2 执行offset commit回调
offsetCommitCallbackInvoker.executeCallbacks();
//1.3 更新partition metadata的leader Epoch
Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets = commitEvent.offsets();
log.debug("Committing offsets: {}", offsets);
offsets.forEach(this::updateLastSeenEpochIfNewer);
if (offsets.isEmpty()) {
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(null);
}
//1.4 添加event,并返回CompletableFuture
applicationEventHandler.add(commitEvent);
return commitEvent.future();
}
rebalance流程
Kafka支持多consumer并行消费多个partition,因此当consumer数量或partition发生变化时,broker端会重新为当前消费Group分配所订阅的partition。
新版rebalance协议细节可见:# KIP-848: The Next Generation of the Consumer Rebalance Protocol