Java SPI机制学习与常用框架SPI案例
概念
SPI(Service Provider Interface)是JDK内置的服务提供机制,常用于框架的动态扩展,类似于可拔插机制。提供方将接口实现类配置在classpath下的指定位置,调用方读取并加载。当提供方发生变化时,接口的实现也会改变。Java生态中JDK、Dubbo、Spring等都通过SPI提供了动态扩展的能力。
样例
public interface Search {
void search();
}
public class FileSearchImpl implements Search {
@Override
public void search() {
System.out.println("file search...");
}
}
public class DataBaseSearchImpl implements Search {
@Override
public void search() {
System.out.println("db search");
}
}
public class SpiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServiceLoader<Search> searches = ServiceLoader.load(Search.class);
searches.forEach(Search::search);
}
}resources文件夹创建META-INF/services/wang.l1n.spi.Search文件,内容为接口实现类:
wang.l1n.spi.FileSearchImpl
wang.l1n.spi.DataBaseSearchImpl运行结果:
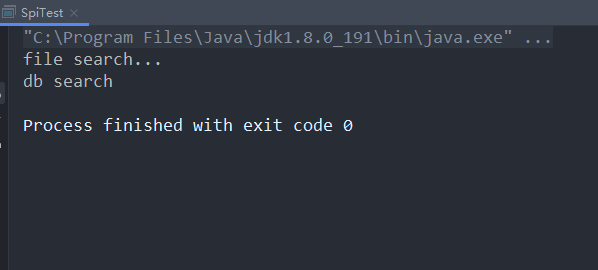
load加载流程
ServiceLoder.load静态方法用于加载SPI实现类,实现逻辑如下:
- 获取当前线程类加载器和上下文信息,调用实例化方法,重新加载SPI
- 重新加载SPI的流程:
- 清空缓存providers中已实例化的SPI服务,providers是LinkedHashMap类型,用于保存已经被成功加载的SPI示例对象
- 如果providers非空,直接返回Iterator,否则返回LazyIterator的Iterator。
- 创建LazyIterator懒加载迭代器,传入SPI类型和类加载器
- 清空缓存providers中已实例化的SPI服务,providers是LinkedHashMap类型,用于保存已经被成功加载的SPI示例对象
实现代码和对应的成员变量如下:
public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> load(Class<S> service) {
ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
return ServiceLoader.load(service, cl);
}
public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> load(Class<S> service,
ClassLoader loader)
{
return new ServiceLoader<>(service, loader);
}
private ServiceLoader(Class<S> svc, ClassLoader cl) {
service = Objects.requireNonNull(svc, "Service interface cannot be null");
loader = (cl == null) ? ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() : cl;
acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null) ? AccessController.getContext() : null;
reload();
}
public void reload() {
providers.clear();
lookupIterator = new LazyIterator(service, loader);
}
private static final String PREFIX = "META-INF/services/";
// The class or interface representing the service being loaded
private final Class<S> service;
// The class loader used to locate, load, and instantiate providers
private final ClassLoader loader;
// The access control context taken when the ServiceLoader is created
private final AccessControlContext acc;
// Cached providers, in instantiation order
private LinkedHashMap<String,S> providers = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// The current lazy-lookup iterator
private LazyIterator lookupIterator;public Iterator<S> iterator() {
return new Iterator<S>() {
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,S>> knownProviders
= providers.entrySet().iterator();
public boolean hasNext() {
if (knownProviders.hasNext())
return true;
return lookupIterator.hasNext();
}
public S next() {
if (knownProviders.hasNext())
return knownProviders.next().getValue();
return lookupIterator.next();
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
};
}LazyIterator加载流程
加载流程参考代码注释:
private class LazyIterator
implements Iterator<S>
{
Class<S> service;
ClassLoader loader;
Enumeration<URL> configs = null;
Iterator<String> pending = null;
String nextName = null;
private LazyIterator(Class<S> service, ClassLoader loader) {
this.service = service;
this.loader = loader;
}
private boolean hasNextService() {
if (nextName != null) {
return true;
}
if (configs == null) {
try {
//获取接口的全称,拼接了META-INF/services/
String fullName = PREFIX + service.getName();
//类加载加载文件内容
if (loader == null)
configs = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fullName);
else
configs = loader.getResources(fullName);
} catch (IOException x) {
fail(service, "Error locating configuration files", x);
}
}
//解析文件内容,获取SPI接口的实现类名
while ((pending == null) || !pending.hasNext()) {
if (!configs.hasMoreElements()) {
return false;
}
pending = parse(service, configs.nextElement());
}
nextName = pending.next();
return true;
}
private S nextService() {
if (!hasNextService())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
String cn = nextName;
nextName = null;
Class<?> c = null;
try {
//获取Class对象
c = Class.forName(cn, false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not found");
}
if (!service.isAssignableFrom(c)) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not a subtype");
}
try {
//使用newInstance创建对象,并添加到providers缓存中
S p = service.cast(c.newInstance());
providers.put(cn, p);
return p;
} catch (Throwable x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " could not be instantiated",
x);
}
throw new Error(); // This cannot happen
}
}JDK SPI能实现加载扩展接口的基本要求,存在几个缺点:
- 需要遍历所有class并进行实例化,需要调用某个特定实现只能循环找。
- 无法和Spring提供的上下文融合使用。
- ServiceLoader类非线程安全
常用框架SPI案例
Spring Boot
org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader#loadFactoryNames方法用于加载所有META-INF/spring.factories文件,主要流程如下:
- 搜索classpath下所有
META-INF/spring.factories配置文件 - 解析文件,获取文件中对应的全限定类名
代码注释如下:
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
//读取缓存
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
//获取文件路径
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
//遍历所有路径
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
解析获取Properties对象
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
//解析properties,存放到map中
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)));
cache.put(classLoader, result);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
}Dubbo
Dubbo并未使用Java SPI,基于SPI机制实现了了功能更强的ExtensionLoader,核心模块位于:org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader 配置文件需要放在META-INF/dubbo下,以如下配置为例:
optimusPrime = org.apache.spi.OptimusPrime
bumblebee = org.apache.spi.Bumblebeepublic class DubboSPITest {
@Test
public void sayHello() throws Exception {
ExtensionLoader<Robot> extensionLoader =
ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Robot.class);
Robot optimusPrime = extensionLoader.getExtension("optimusPrime");
optimusPrime.sayHello();
Robot bumblebee = extensionLoader.getExtension("bumblebee");
bumblebee.sayHello();
}
}下面简要一下Dubbo SPI的核心类ExtensionLoader的实现。
核心成员变量
LoadingStrategy[] strategies:配置文件加载策略。ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, ExtensionLoader<?>> EXTENSION_LOADERS:每个扩展接口对应一个ExtensionLoader实例,该集合缓存了所有Loader实例。ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, Object> EXTENSION_INSTANCES:该Map缓存了扩展实现类与对应实例对象的映射关系
LoadStrategy
Subbo在加载SPI实现类时存在优先级,当前存在三个实现: 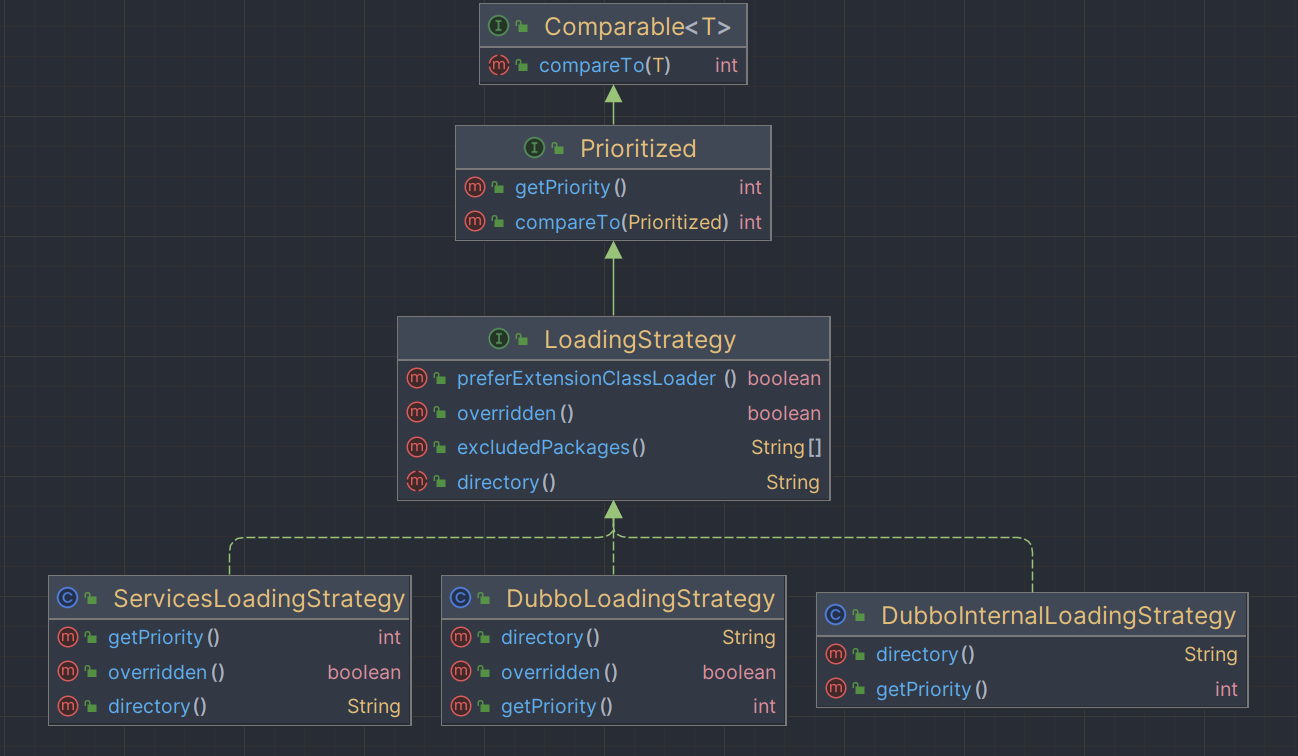
配置文件目录有以下三个位置: 1. META-INF/dubbo:由DubboLoadingStrategy负责,用户自定义SPI配置文件 2. META-INF/services:由ServicesLoadingStrategy负责,兼容JDK SPI 3. META-INF/dubbo/internal:由DubboInternalLoadingStrategy负责,Dubbo内部使用的SPI配置文件
核心实现
Dubbo SPI的核心实现方法为:org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader#getExtension
public T getExtension(String name) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension name == null");
}
if ("true".equals(name)) {
//获取默认的扩展实现类
return getDefaultExtension();
}
//从cachedInstances<name, Holder<>>
final Holder<Object> holder = getOrCreateHolder(name);
Object instance = holder.get();
//double check
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (holder) {
instance = holder.get();
if (instance == null) {
//若未创建实例,则创建并set
instance = createExtension(name);
holder.set(instanc e);
}
}
}
return (T) instance;
}
在createExtension()方法中实现了SPI配置文件的查找已经对应实现类的实例化,同时还实现了自动装配以及自动Wrapper包装等功能:
- getExtensionClasses()会获取cachedClass缓存,根据扩展名获取对应的实现类,如果未初始化,则调用loadExtensionClasses()加载实现类。
- 自动装配扩展对象的属性(injectExtension()方法)
- 自动包装扩展对象
//扩展实现类的加载过程
private T createExtension(String name) {
Class<?> clazz = getExtensionClasses().get(name); // 1
if (clazz == null) {
throw findException(name);
}
try {
T instance = (T) EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz);
if (instance == null) {
EXTENSION_INSTANCES.putIfAbsent(clazz, clazz.newInstance());
instance = (T) EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz);
}
injectExtension(instance); // 2
//3
Set<Class<?>> wrapperClasses = cachedWrapperClasses;
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(wrapperClasses)) {
for (Class<?> wrapperClass : wrapperClasses) {
instance = injectExtension((T) wrapperClass.getConstructor(type).newInstance(instance));
}
}
initExtension(instance);
return instance;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Extension instance (name: " + name + ", class: " +
type + ") couldn't be instantiated: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}getExtensionClasses()实现:
private Map<String, Class<?>> getExtensionClasses() {
Map<String, Class<?>> classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
synchronized (cachedClasses) {
classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
classes = loadExtensionClasses();
cachedClasses.set(classes);
}
}
}
return classes;
}
private Map<String, Class<?>> loadExtensionClasses() {
cacheDefaultExtensionName();
Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses = new HashMap<>();
for (LoadingStrategy strategy : strategies) {
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, strategy.directory(), type.getName(), strategy.preferExtensionClassLoader(), strategy.overridden(), strategy.excludedPackages());
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, strategy.directory(), type.getName().replace("org.apache", "com.alibaba"), strategy.preferExtensionClassLoader(), strategy.overridden(), strategy.excludedPackages());
}
return extensionClasses;
}